Verity VM Installation (VMware 7.0.3)🔗
Introduction🔗
The Verity management and orchestration system is comprised of three functional components, all of which are instantiated as Virtual Machines (VMs). This document describes the installation and configuration of these VMs within a VMWare ESXi server.
Prerequisites🔗
Resource Calculator🔗
Use the Verity VM Resource Calculator to determine system resources.
Virtual Machine Overview🔗
Verity’s three VM functional components:
| Virtual Machine | Function |
|---|---|
| Virtual Network Commander (vNetC) | Orchestration logic, GUI hosting, northbound RESTful API, and databases. |
| Software Defined LAN Controller (SDLC) | The SDLC VM is comprised of a series of containers that map one-to-one to the managed switch devices. Network discovery, device provisioning, and network assurance. The SDLC serves as the abstraction layer between the managed switch and the vNetC by translating the native management protocols into the vNetC’s NETCONF interface and Yang model. |
| Satori | The Satori VM is comprised of various containers that collect, process and display the network device details that are managed by Verity. |
Virtual Machine Topology🔗
Below is the basic VM and hardware topology for reference: 
Public IP Addresses
The standard installation assumes private IP addresses are use by the Verity components and the managed switches. If that is not the case, refer to details in the section "Configure vNetC from the Console" below.
The following diagram shows the recommended management network architecture. Variations are possible based on individual customer’s network needs.

Install vNetC VM🔗
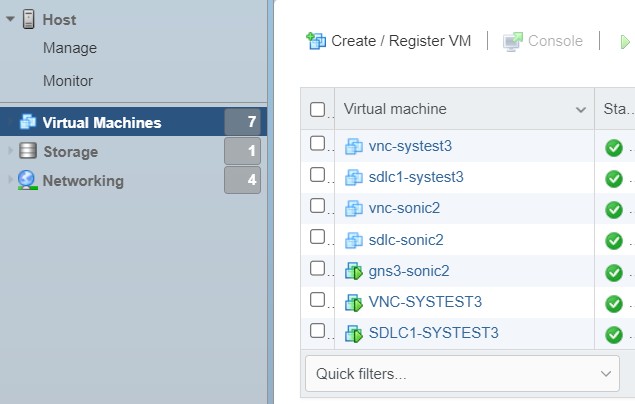
- Go to Virtual Machines.
- Click Create/Register VM.
- In the window that appears select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file.
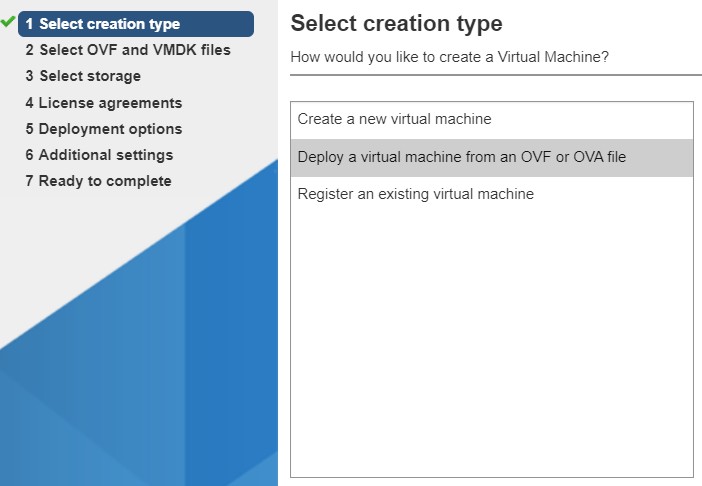
- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the VM and upload the vNetC VM Image OVA file via the prompt that says Click to Select file or drag/drop.
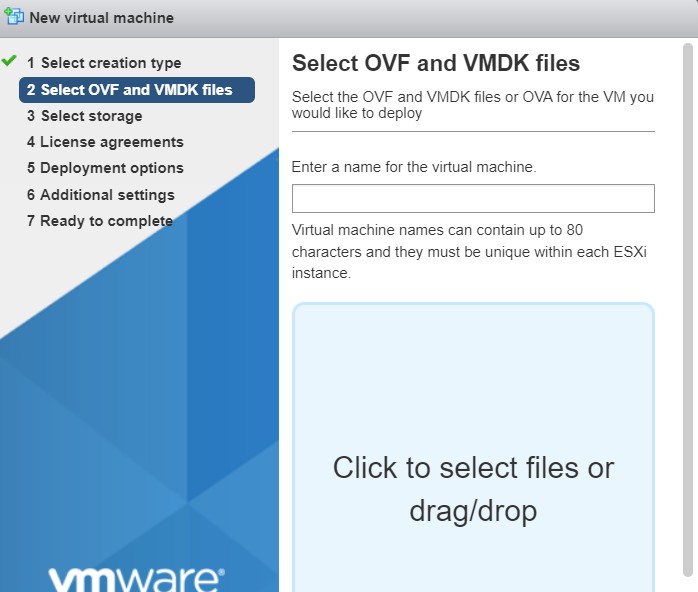
- Click Next.
- Select the desired data store options. Click Next.

- Set the Deployment options and network mappings to the correct Port Group.
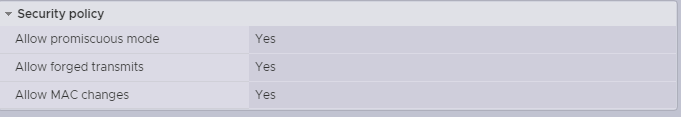
 . This Port Group must be set to promiscuous mode.
. This Port Group must be set to promiscuous mode. - Click Next.
- Review the settings and if they are correct, click Finish.

- The VM creation process will start. When the process completes the progress bar in Recent tasks at the bottom of the screen will say Completed Successfully.

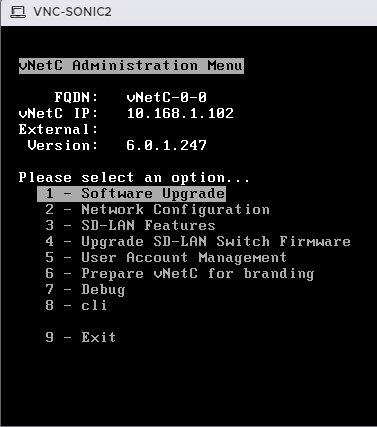
Configure the vNetC from the Console🔗
This step requires you to configure the vNetC with an IP address and Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). To do so, you need to open the VM console.
- Select your VM under the Virtual Machine column and click Console/Open browser console.

- The VM console appears. The vNetc initialization may take several minutes. While waiting you can press Enter and wait for login prompt.
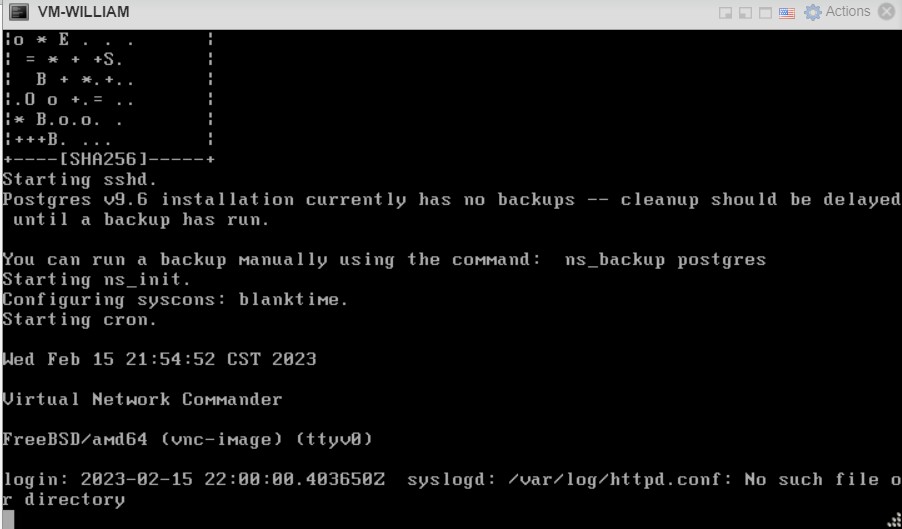
- Login to the vNetC with username root and password vnc1234.
- Enter a new password if prompted (new password = vnc1234). If not prompted for the password, you can continue to use the default password or change it with the passwd command.
- Run the administration application from the shell by typing ns_admin and pressing Enter.
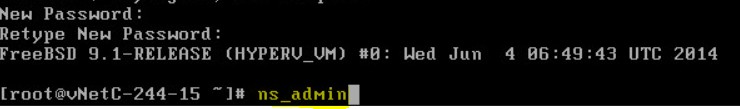
- You are prompted to enter a web user interface admin account password (ex. admin). Document the password you choose as it will be required for GUI authentication later in the process. It is very important that you remember the password!
-
Press Enter when complete.
- Press Enter.
- Select FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name). Press Enter and set to the desired Fully Qualified Domain Name. If the field is prepopulated, it is required that you replace the default text with your own FQDN.
- Verify that WAN IP DHCP is disabled. If WAN IP DHCP is enabled, disable it using the menu.
- Select WAN Static IP Settings, press enter.
- Enter the following information:
- IPv4 Address and subnet in CIDR format (x.x.x.x/#)
- Default Route (Gateway)
- DNS Server 1 & DNS Server 2 (optional)
- Return to the network configuration menu.
- Save Settings.
- Follow the prompt and the VM will reboot with the new settings configured.
Public IP Addresses
The standard installation assumes private IP addresses are use by the Verity components and the managed switches. If that is not the case, refer to the instructions below.
- ssh back into the vNetC as the root user
-
copy the following string and paste into the command line
ns_vnc_setup --features acs_tunnel=1
Install the License (required) and Upgrade to the Latest vNetC Core Software🔗
- Use Chrome Web Browser to access the vNetC IP address that was just configured.
- At the login prompt enter username admin and the administration password configured in the menu during installation. These are the credentials you entered in step 3 of Configure the vNetC from the Console.

- When the window appears, record the information on the Licensing tied to line. Provide this information to BE Networks to obtain your license file.

- After you obtain your license.cms file you are required to upload it to the application. In the License window select data center or campus (depending on your system). Use the drag and drop palette to upload the file or browse for the file. The license file may also be embedded in a \<filename>.tar file and this can also be directly imported and the system will extract the license.cms file.
- After you upload the file make sure a success message is presented.
- Click the button that says Yes to confirm the restart.
- After the Verity window has fully completed populating select the Administration button (lower left).
- Select Software Packages tab (top of screen) and click vNetC Packages.
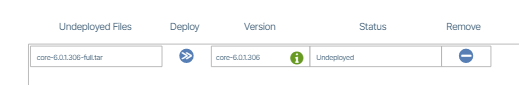
- Using the Browse Files (or drag and drop) field, import the vNetC Core Upgrade file provided by BE Networks.
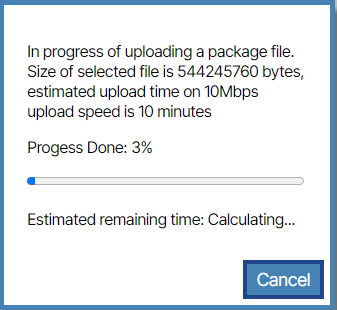
- When the process is complete you are presented with a success message.
- Click the Deploy button.
- When prompted to continue, click Yes. The software updates.
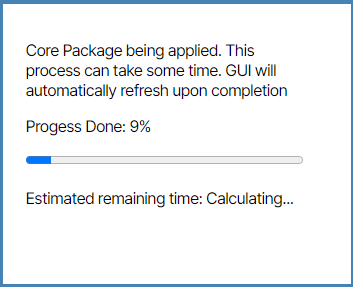
Temporary Error Message
You may see an error titled Fatal Error WebSocket Error: Connection lost -2 appear, this is normal. The browser may temporarily say that the site cannot be reached. When the process is done the landing page will render.
- If you see a migrations prompt click Accept.
 .
. - If you see a tan prompt that says GuiA not attached, no GuiA Switch, clear the message by clicking it.
- The display should look like the following image:

- Go back to the VNC Console in VMware and type
poweroffin the CLI. This will cleanly shutdown the VNC.
Congratulations
You have now successfully installed the VNetC VM.
Install SDLC VM🔗
SDLC NIC Mapping when using vCenter
When deploying the SDLC with vCenter, the NIC to MAC mapping can be remapped, causing connectivity issues with the SDLC and vNetC. If using vCenter to deploy the OVA, check the NIC Mapping on the SDLC by logging in to the SDLC's console, and going to Administration -> Network -> NIC-Map and enter show to see mapping:  Verify that the MAC Address for the NIC's in the Mapping match with what the MAC Addresses in VMWare say:
Verify that the MAC Address for the NIC's in the Mapping match with what the MAC Addresses in VMWare say:  If changes are required, use the
If changes are required, use the edit command and select the Index number and map it to the correct MAC Address.
- Go to Virtual Machines. Click Create/Register VM.

- In the window that appears select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file.

- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the VM and upload the SDLC VM Image OVA file via the prompt that says Click to Select file or drag/drop. Click Next.

- Select the desired data store options. Click Next.

- Set the deployment options. Click Next.

- Review the settings and if they are correct, click Finish.

- The VM creation process will start. Wait until you see the message Completed Successfully.

Configure SDLC (Console)🔗
The SDLC must be configured with a Static IP address and the vNetC FQDN.
- Select the SDLC from the VMWARE ESXi interface and click the Console tab.
- Select Open browser console.

-
DHCP Error Messages
During the following process DHCP errors may appear. These can be ignored.
-
Press Enter to get the login prompt, enter username: admin and password: admin.
- At the command line interface (CLI) press Enter to see a list of options.
- Select admin and press Enter.
- Type Wizard and press Enter.
Note
If vNetC and SDLC (GuiA, ACS) are on different subnets, it is recommended to have three consecutive static IP addresses on the same subnet for GuiA, ACS and DHCP. However, if vNetC is on the same subnet as GuiA, ACS and DHCP, it is recommended to use four sequential IP addresses.
| Prompt | Answer |
|---|---|
| Enter new hostname | SDLC |
| Enter MGMT IP or enter 'd' to use DHCP | Enter management IP |
| Enter URL connection protocol | http |
| Enter default gateway IP/Prefix in CIDR format | Enter the default gateway IP address |
| Enter ACS IP or type 'none' to remove config | Enter IP |
| Enter vNetC FQDN or IP | vNetC IP address |
| Enter DNS server | Enter DNS server IP |
| Enter comma separated NTP server(s) | Enter vNetCs IP address |
| Enter ACS url | Press Enter or Enter a different url |
- Type y and press Enter
- Reboot is required for any changes to take effect. In the console, type reboot and press Enter.
Power On the vNetC🔗
- In the VMware ESXi interface power on the vNetC. This takes a few minutes.
- Open the GUI and select select the Admin Settings option.

- Set up the Management VLAN used to access the Management network. This field is required even if your management switches are using untagged connections.
-
For Permissible IP Address Ranges on Managed Devices enter the relevant IP address range (IP address and Mask).

Permissible IP Range Requirement
The range entered MUST include SDLC components.
-
Click the Save button to save your settings. (
 ).
). - Wait until the process is finished. The application landing page resembles the image below when all processes have been completed.

Update SDLC🔗
- In Topology/Topology set the Upgrades selection button to the Enable setting
 .
. - Click the Admin tab. Under the Software Packages column double-click Image Packages.
- Select and place the SDLC Binary Firmware Upgrade firmware file on the Drag & Drop area or use the Browse Files button to select the file.
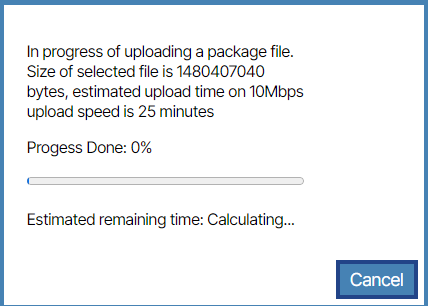
- When uploaded, you are prompted with a green success message.

- Deploy the upgrade by clicking the Deploy button.

- A validation message appears. Click Yes.

- Wait while the package is applied.
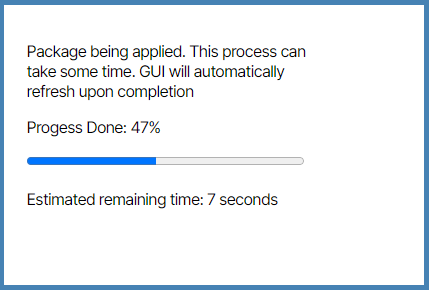
- Click Admin and click VNFs .

- Double click the SDLC section.

- Double click the box with the title of SW Version.

- Set the Target Package field to the Firmware version
 .
. - Click the Save button (
 ).
). - Click Yes to the validation message.
- Let the process complete.
- When the window appears the initial state of System Applications are offline. When the System Applications come online their LED icons render green. This may take up to 5 minutes. Admin/VNFs

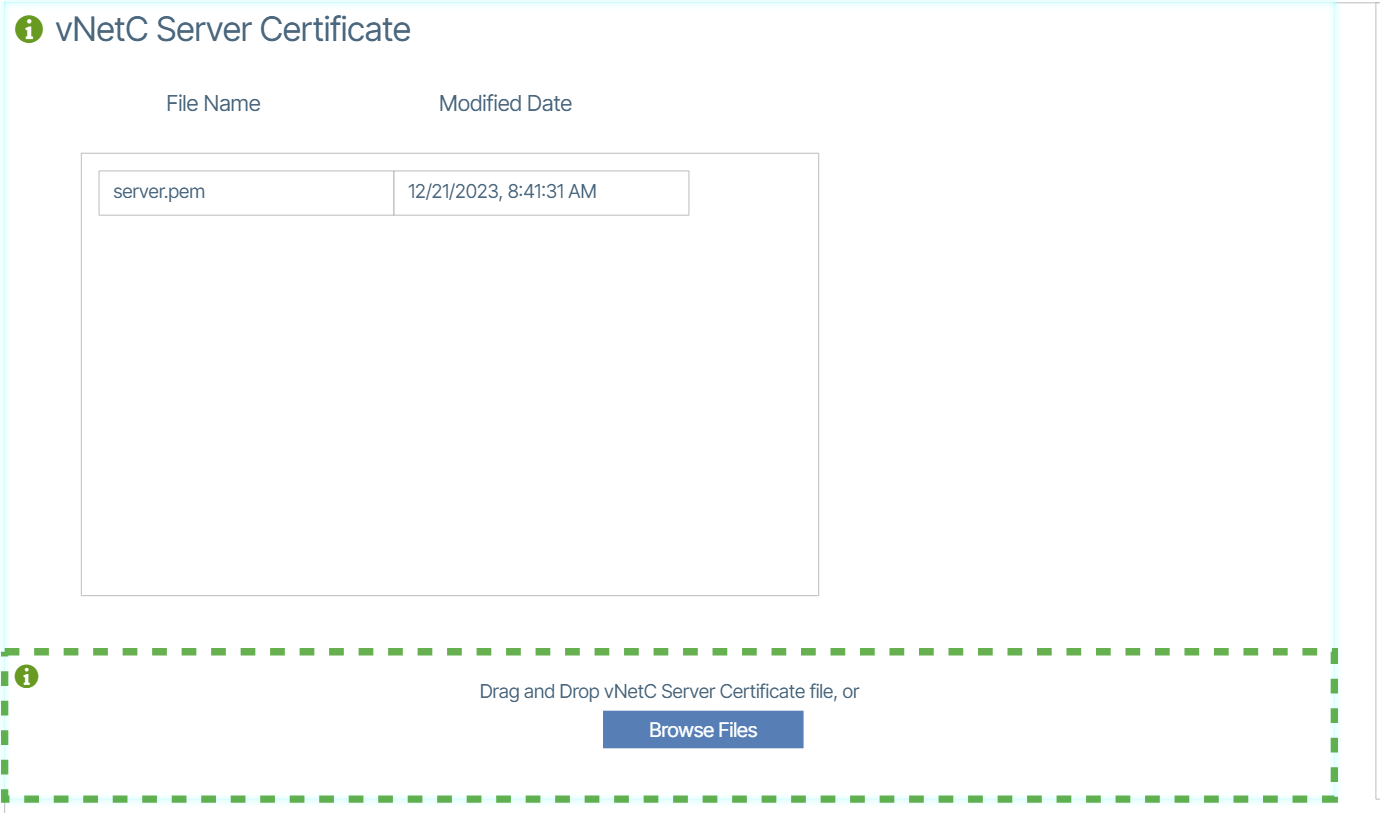
Site Certificate🔗
In order to avoid having to accept the self signed certificate delivered with the system you will need to add a server.pem file to the system. This will need to be obtained from your internet domain administrator.
Install Satori VM🔗
- Go to Virtual Machines.
- Click Create/Register VM.

- In the window that appears select Deploy a virtual machine from an OVF or OVA file.

- Click Next.
- Enter a name for the VM and upload the Satori VM OVA file via the prompt that says Click to Select file or drag/drop.

- Click Next.
- Select the desired data store options.

- Click Next.
- Set the Deployment options – Network mappings to the correct Port Group.
- This Port Group must be set to promiscuous mode.
- Click Next.

- Review the settings and if they are correct.

- Click Finish.
- The VM creation process will start. When the process completes the progress bar in Recent tasks at the bottom of the screen will say Completed Successfully.

Configure Satori VM (Console)🔗
Prerequisites🔗
- Operating System: Ubuntu Linux (or compatible Linux distribution)
- Shell: Bash shell environment
- Satori Admin Script:
satori_admin.sh - Permissions: Execute permissions on the script file
- Network Configuration: You must configure the settings at Admin/Admin Setting (
 ) to allow access for the subnet where Satori will be installed.
) to allow access for the subnet where Satori will be installed. - Dependencies: The following scripts must be present in the same directory:
setup.sh- System setup scripttroubleshooting.sh- Troubleshooting utilities script
Installation & Setup🔗
This step requires you to configure Satori with an IP address, default gateway, and DNS servers. Then the script will ask for the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the VNetC so it knows how to connect the Satori dashboard. To do so, you need to open the VM console.
- Select your VM under the Virtual Machine column and click Console/Open browser console.

- The VM console appears. The Satori initialization may take several minutes. While waiting, you can press Enter and wait for login prompt.
- Login to Satori with username verity and password vnc1234.
- Enter a new password. Remember this password.
- Run the setup application from the shell by typing sudo ./satori_admin.sh and pressing Enter. You will see the following interface:
****************************************
Welcome to the Satori Admin Menu
****************************************
Please choose an option:
1) setup
2) troubleshooting
#?
Satori Admin Menu🔗
Option 1: Setup🔗
Purpose: Executes the system setup process
When to Use:
- Initial system configuration
- Reinstalling or reconfiguring components
- Setting up new environments
Troubleshooting
For further information about Troubleshooting, visit the Troubleshooting section.
Select Setup🔗
- When prompted with
#?, enter the number corresponding to your choice: 1 forsetup. -
Press
Enterto confirm your selection -
When prompted, enter the following information:
- IPv4 Address and subnet in CIDR format (x.x.x.x/#)
- Default Route (Gateway)
- DNS Servers seperated by a comma
- Enter the hostname of the server
- Enter the FQDN or IP address of the vNetC host.
- Setup of Satori is complete. The display will show the current settings and provide a message on how to make changes in the future.
- Type sudo reboot to reboot the VM for all the settings to take effect. After the reboot, it takes about 3 minutes for the Docker containers to start up and to announce itself to the vNetC.
- When the Satori VM connects to the vNetC, in Verity, a Growl with the MAC Address of the Satori VM will appear. Once this does, use the refresh button on Chrome.

- There will be a new Satori menu option available. Also, the Satori Dashboard will be the new startup screen.

Upgrade to the Latest Satori Software🔗
Warning
After completing the previous installation steps, the user must install the latest software as outlined below. The installation process is not considered complete until this final step is finished.
- Upgrade the Satori software via the vNetC Web Administration.
- Use Chrome Web Browser to access the vNetC IP address that was just configured.
- At the login prompt enter username admin and the administration password configured in the menu during installation. These are the credentials you entered in step 3 of Configure the vNetC from the Console.

- From the Admin web page and under the Software Packages heading, click App Packages.

- Using the Browse Files (or drag and drop) field, import the Satori Upgrade file provided by BE Networks.


- When the process is complete you are presented with a success message.


- Click the Deploy button.
- When prompted to continue, click Yes. The software updates.

Wait for System
It take about 5 minutes for the tarball to be uploaded to the Satori VM, and the changes to be applied and the new containers started up. If you SSH into the Satori VM, and go to the /be_install directory, you will see the tarball uploaded. If you run sudo docker ps you will see the uptime of the containers to be less than 5 minutes online letting you know that everything is updated. [Tell user how to view Satori version].
Congratulations
Verity has been successfully installed. Treat yourself to an iced coffee!